Artificial intelligence (AI) is already present in plenty of applications, from search algorithms and tools you use every day to bionic limbs for the disabled. Cognitive computing is a term used by IBM. Computers aren’t really cognitive, however. What are AI and cognitive computing and how are various forms of AI used and developing?
Artificial intelligence is here for a long time in many forms and ways. In recent years significant progress has been made in some areas of AI. This doesn’t mean that AI, in general, is evolving as fast, just those fields. And some of them are increasingly used for different domains of digital transformation.

Instead of talking about artificial intelligence (AI), some describe the current wave of AI innovation and acceleration with – admittedly somewhat differently positioned – terms and concepts such as cognitive computing. Others focus on several real-life applications of artificial intelligence that often start with words such as “smart” (omnipresent in anything related to the Internet of Things and AI), “intelligent,” “predictive” and, indeed, “cognitive,” depending on the exact application – and vendor.
Artificial intelligence is essential for and in, among others, Industry 4.0, information management, digital health, and life sciences, big data analysis, security (cybersecurity and others), various consumer applications, next-gen smart building technologies, FinTech, predictive maintenance, robotics and so much more. In other words: in very diverse areas where data and information are essential.
On top of that, AI is added to several other technologies, including IoT, to unlock the full value of these technologies in several applications and processes.
The historical issue with AI – is cognitive better?
There are many reasons why several vendors doubt using the term artificial intelligence for AI solutions/innovations and often package them in another term (trust us, we’ve been there).
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a term that has somewhat of a negative connotation in general perception but also in the perception of technology leaders and firms.
One major issue is that artificial intelligence – which is really a broad concept/reality, covering many technologies and realities – has become like a thing, just like ‘the cloud’ or ‘the Internet of Things’, we talk about and also seem to need to have an opinion/feeling about, with thanks to, among others, popular culture. Hollywood loves AI (or better: superintelligence, not the same). It makes for good sci-fi blockbusters and movies where non-human ‘things’ such as robots take over the world.
Fast growing AI technologies for consumer facing industries include chat bots and Virtual Personal Assistants (VPA) and smart advisors.
The fact that AI is such a broad concept leads to misunderstandings about what it exactly means. Some people are really speaking about machine learning when they talk about AI or about deep learning or about text mining, the list goes on. Others essentially talk about analytics and in doomsday movie scenarios everything gets mixed, including robotics and superintelligence. And in most cases we really talk about some form of AI.
This phenomenon goes hand in hand with the fact that artificial intelligence has failed to deliver upon expectations from previous ‘popularity waves’ (going back to the previous Millennium, see box below this article) and is really old as a concept, research field and set of technologies – making it less appealing for many vendors, as obviously AI technologies and applications, as well as expectations, have evolved, albeit less than some like us to believe.
Still, deep learning, image recognition, hypothesis generation, artificial neural networks, they’re all real and parts are used in various applications. According to IDC, cognitive computing is one of six Innovation Accelerators on top of its third platform. You’ll notice IDC speaks about cognitive too (more about the meaning of cognitive systems as an innovation accelerator further in this article).
Artificial intelligence is being used faster in many technological and societal areas although there is quite some hype about what “it” can do from vendors. Still, the increasing attention and adoption of forms of AI in specific areas triggers debates about how far we want it to go in the future.
Prominent technology leaders have warned about the danger and think tanks and associations have been set up to think about and watch over the long-term impact of AI (and robotics) with discussions on the future of humanity and the impact of superintelligence but also, closer to today’s concerns, impact of automation/AI/robots on employment. Anyway, it again adds to that mix of ingredients that creates the conditions to strengthen the negative connotation regarding the term artificial intelligence – and as current political shifts show automation/digitalization as a whole.
If it makes us feel more comfortable to talk about “intelligent”, “cognitive” or “smart” anything, so be it. What matters more is how artificial intelligence is here and increasingly will be, why it’s here, how it helps and is used and what it can mean for you.
AI in context: how it interacts with other transformational technologies
When people try to explain that artificial intelligence is already here since a long time in some form, they often refer to the algorithms that power Google’s search technology. Or an avalanche of apps on mobile devices. Strictly speaking, these algorithms are not the same as AI though.
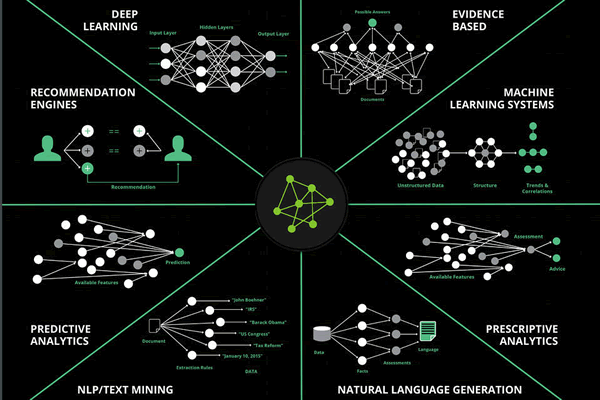
Also think about speech recognition, for instance. Or identification technologies, product recommendations and even the electronic games we play. And of course there are many examples, depending on industry or function. Marketing, for instance, uses a bunch of platforms with forms of AI: from the sentiment analysis in social platforms to the predictive capabilities in data-driven marketing solutions.
So, artificial intelligence is many things. A graphic from research by Narrative Science shows various areas in the broader ecosystem of AI, ranging from text mining to deep learning and recommendation engines. The latter is something everyone knows or at least uses with recommendation engines being literally everywhere. And then there are all those apps such as Uber, Airbnb and the likes that connect you with respectively an Uber driver in the neighborhood and an Airbnb place to stay – powered by AI.
To understand the role and current wave of AI in today’s and tomorrow’s business and society context it’s important to look at the realities and technologies underneath the big overlapping umbrella term. It’s also important to see the current wave of artificial intelligence in a context of big data, unstructured data, integration and digital transformation.
One of the reasons why artificial intelligence – maybe not the term – has become so hot right now is the fact that it is a perfect fit for – and even indispensable enabler of – other technologies and the possibilities they offer. Sometimes you just need artificial intelligence techniques.
The interconnectedness of 3rd platform technologies and AI
As we don’t feel the urge to reinvent the lists of technologies that enable and accelerate digital transformation and innovation, we’ll use IDC’s previously mentioned famous 3rd platform, although you can use many others.
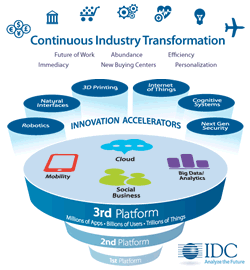
The foundation of that so-called 3rd platform consists of 4 sets of technologies that are interconnected and de facto inherently connected with AI as well.
As a reminder: the high interconnectivity of technologies and processes in real-life applications is a core trait of what we’ve come to known as the digital transformation or DX economy.
Each of these sets of technologies (they are not things either but just as AI consist of several technologies and, more importantly, applications and consequences) are technological drivers of digital transformation as such.
On top of these 4 foundational sets or pillars (cloud computing that is essential in AI, mobility, social and big data analytics) come so-called innovation accelerators, the term we used before.
These are again various – and ever more – sets of technologies and technological innovations that drive digital transformation and all of them are inherently integrated with artificial intelligence and in reality some are even close to synonyms of AI.
Cognitive systems: an innovation accelerator
One of these innovation accelerators, as you can see in the image of the 3rd platform, are so-called cognitive systems technologies themselves.
Cognitive computing is really a term that has been popularized by mainly IBM to describe the current wave of artificial intelligence and, specifically also machine learning, with a twist of purpose, adaptiveness, self-learning, contextuality and human interaction. Human is key in here and without a doubt also easier to digest than all those AI-related doomsday movie scenarios.
Essentially, cognitive systems analyze the huge amount of data which is created by connected devices (not just IoT) with diagnostic, predictive and prescriptive analytics tools which observe, learn and offer insights, suggestions and even automated actions. As you probably know, a pillar of IBM’s view is IBM Watson as we’ll tackle below.
The term ‘cognitive computing’ strictly speaking is a conundrum. Cognition, for instance, also includes the subconscious which is in fact a major part of cognition. Although this would bring us too far it needs to be said that IBM does make exaggerated claims about what its ‘cognitive’ platform Watson can do. Marketing indeed. People have some typical characteristics that AI isn’t able to understand. A simple example: as far as we know we’re still the only species that knows it exists (within the limits of what human knowledge is able to know, more food for discussion with transhumanists). Human emotions are also about more than brains and intelligence. Emotions, often irrationally conflicting, can’t be reduced to math and the whole comparison of people as machines is really flawed.
Cognitive computing and AI powering digital evolutions
Other innovation accelerators where AI fits in include the Internet of Things. Here as well, AI and cognitive computing or cognitive systems are omni-present.
AI and the Internet of Things
Once you start connecting everything you need APIs, connectors, information analysis technologies and “embedded intelligence”, essentially code that makes it all possible.
Moreover, the Internet of Things, which really is about automation and information (with on top of that a layer of possibilities to, for instance, enhance customer experience or make life a bit easier) adds loads of data, Big Data (one of the four pillars of the 3rd platform) to an already exploding digital data universe. The majority of all that data is unstructured and needs to be turned into knowledge and (automated) actions as good old rules-based information management approaches simply can’t handle it (remember the DIKW model). Guess what is needed to make it possible and to even make all these other aspects of the Internet of Things possible? Indeed: artificial intelligence.
The future of security is intelligent too – AI in cybersecurity
We won’t cover all the other innovation accelerators except one: next generation security.
Do you remember that cybersecurity was – and often still is – seen as a range of “defensive” solutions and approaches (from strategies to technologies such as firewalls and anti-virus apps)? Well, that is changing.
Security is becoming more holistic, also looking at the human aspect and all elements in a changing security perimeter. But most of all: cybersecurity business strategy is becoming more pro-active and technologies to predict cyberattacks before they even happen are in high demand. What do they use: indeed, artificial intelligence, not in the ‘big overlapping’ AI sense but in detecting patterns in data (and thus potential attacks) and acting upon this data. AI, however, is also a security concerns. In high-profile attacks in an industrial context AI patterns were found in the malware. When deep learning comes in here, that’s a pretty scary place to be.
Cognitive and AI in the age of data and analytics
AI and cognitive aren’t just present in that innovation accelerator layer. It is, as said, also very present in the four pillars of the third platform that are driving and enabling digital transformation just as they changed the ways we, businesses and consumers, behave, work and innovate.
We already mentioned Big Data in that context: ever more unstructured data. The solution: AI. Moreover Big Data as such isn’t the crux of the matter. For years we know that most of all Big Data Analytics matter. Turning data into outcomes knowledge, actions, insights etc. That analytics part is so important that IDC has called the Big Data pillar the Big Data/Analytics pillar. What is needed for these analytics? Indeed, again AI techniques. In fact, analytics is also what so-called cognitive systems are all about in a very high degree.
AI/cognitive and unstructured data/content
The picture is clear. But what does it all mean in practice? Let’s use data again.
In the end, the other pillars of the 3d platform and technologies driving digital transformation are a lot about data to. The cloud, mobility, social business and collaboration…
Unstructured and semi-structured data is fueling a renaissance in the handling and analysis of information, resulting in a new generation of tools and capabilities that promise to offer intelligent assistance, advice, and recommendations to consumers and knowledge workers around the world.
We mentioned earlier how the data universe is exploding with unstructured data growing much and much faster than other data (strictly speaking all data is structured one way or the other but when thinking structured data mainly think text, images and so forth). This is, among others due to, mobile data traffic and the Internet of Things (see how it is all connected?).
This phenomenon isn’t new either and has been predicted since at least 2000. There are debates about the exact meaning of unstructured data and to what degree it is different from unstructured or semi-structured data. Simply said unstructured data is all the data you would get from IoT sensors, social media (again a link with one of the four pillars), text files (email) and much more. Since several years it is estimated that 80 percent of data is unstructured and that percentage seems to grow as the volume of unstructured data keeps growing faster.
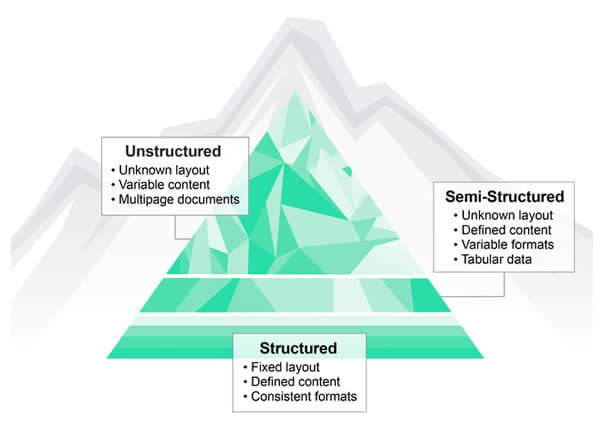
The typical thing with unstructured data is that it doesn’t have a predefined data model as you have with data sitting in a relational database, for instance. Unstructured data and content as such has no meaning or context because in principle we don’t know what it is.
It comes in many shapes and forms and from several sources and is often text-intensive. From paper documents that need to get digitized to Twitter messages or email, also a major source of unstructured data/content. And it’s here that – again – we see various artificial intelligence techniques such as Intelligent Document Recognition or IDR, text mining, self-learning knowledge base technology, machine learning, natural language processing and the whole cognitive computing aspect come into the picture.
In fact, if you look at the page of IBM’s famous Watson platform you’ll read that, qote, “IBM Watson is a technology platform that uses natural language processing and machine learning to reveal insights from large amounts of unstructured data”. In an information management context, we find artificial intelligence in, among others, the mentioned IDR applications, self-learning systems for customer service information, information routing processes, predictive analytics and automated processes such as automated loan application classification.
The value of AI – conclusion and next steps
Artificial intelligence is – and will be – critical for many technological and business evolutions. And, yes, it is one of many enablers of digital transformation.
Should we debate how far we go with it? Yes. But we really need to know what we are talking about.You can learn more about that in our article on the debates regarding AI, its dangers and the future of humanity, essentially revolving around superinterintelligence.
Expect further articles, including a dive into the past, presence and future of AI/cognitive – and the various applications and “forms” of AI.
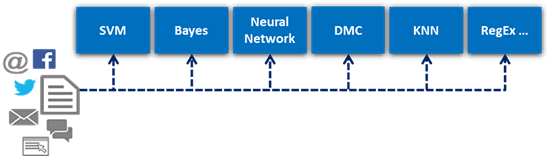
Because, as said artificial intelligence is not a thing. Just looking at one context where AI and cognitive are used, Intelligent Document Recognition, there are several forms of artifical intelligence such as semantic understanding, statistical clustering and classification algorithms such as SVM, Bayes and Neural-Net, as Roland Simonis explained in part three of a blog series for AIIM, reposted here with his kind permission, where he tackles how AI helps solve the information and Big Data challenge.
For now, let’s say it’s clear there is no harm in an algorithm enabling people to find something better (in fact, if you look at how poor search intelligence still is, we’d love to so far more intelligence in it) and there is no harm in having a system that helps you process and understand information faster and better to improve anything worth improving such as customer service (with a growing usage of IDR applications and Knowledge Base technology) and , cybersecurity or people’s health, to name just a few.
But artificial intelligence, as a “whole”, is not as far as we tend to believe with already ample applications of artificial intelligence in business and AI, machine learning and deep learning increasingly being used in a combined approach with related technologies, ranging from advanced analytics and IoT to robotics, and more.

The waves of artificial intelligence

Although some look further in the past for the birth of AI, the 1950s was really when the first wave started. One of the founders of artificial intelligence as a concept was US computer scientist and cognitive scientist Dr. John McCarthy. He is believed to also have coined the term and defined artificial intelligence as “the science and engineering of making intelligent machines”. After a conference in 1956, where McCarthy was present, the first wave really took off, mainly focusing on research. On top of McCarthy, many of these researchers became household names in those early research days and today still are. Among them: Marvin Minsky, Herbert Simon and Allenn Newell, to name a few.
McCarthy’s ideas and those of his peers, as well as years of research and initial developments next led to the second wave of artificial intelligence in the 1980s, mainly due to the success of expert systems, among others strengthened by the rise of the PC and the client-server model.
A third wave took place at the end of the nineties and early 2000 when there was more attention from the perspective of specific applications of AI across diverse domains. On top of that, there was the success of the Internet, which also led to quite some hype and predictions that didn’t really live up to their promises. The spreading availability and usage of the Internet did cause a stir. In those days we worked for a publishing house, as publishers, and one of the company’s major magazines, Inside Internet, had several pieces from AI researchers from various universities where real-life applications were tried. Artificial intelligence was again debated a lot and became popular, also in globally launched magazines in those days such as Wired.
Unfortunately, the hype was big again too. It’s also in those days that the convergence of man and machine became increasing popular(ized). In 1999, for instance, we had the chance to interview Joël de Rosnay who had published a book of a nascent global super organism, the cybiont, which would know a “symbiotic mankind” in a connected ecosystem of humans, technology and everything really. It does sound familiar now, doesn’t it? More about de Rosnay’s and views – and those of others – that show how increasing interconnectedness was seen as the big promise back then in this article.
Today’s artificial intelligence wave is one of rapid adoption of AI technologies in new applications, driven by, among others the mentioned 3rd platform technologies, including the cloud, faster processing capabilities, scalability, Big Data, , IoT, the push of various companies in a space where technologies continue to be refined across several applications and industries (self-driving cars, robotics, the rise of chatbots and more) and, last but not least, market demand for smart and intelligent technologies to leverage the potential of new technologies, information and digital transformation.
In general the main driver and common thread across all of this is the data deluge. Without AI there isn’t that much to do with data to put it simply. Advanced analytics, predictability in areas where traditionally silos exist and decisions are based upon historical data, handling unstructured data are some of these examples. Last but not least there are also the advances in specific forms of artificial intelligence. Deep learning, a form of machine learning, is certainly part of that and by the time you read this we’ll have new developments as things do speed up.
Whether this wave will lead to true and continuing business momentum however remains to be seen despite “good signs”, as is the next wave and the increasing number of dicussions on the “ethics”, security and “place” of AI in the future. The “AI and robots taking over mankind view” and superintelligence evolutions – instead of AI as mimicking possibilities of the human brain for a purpose – are real concerns and deserve attention.
It’s clear that artificial intelligence is indeed not new but has changed a lot and gains more attention than ever. It’s becoming ubiquitous and transforms the way we work, live and do business. Along with robotics (and phenomena such as 3D printing, the Internet of Things, etc.), artificial intelligence is again an increasingly debated topic. Still, this wave is not the last one, it is even very similar in many regards to the previous one and the hype is loud.
Also in artificial intelligence
- Understanding and debating the fears about artificial intelligence
- Will machines with AI replace humans? The Second Machine Age
- AI: the automation of customer interactions with IDR applications and Knowledge Base technology
- AI in sales: usage, impact, examples and evolutions
- The increasing role of artificial intelligence in healthcare delivery evolutions
- Artificial intelligence in business: CIO challenges and recommendations
- Turning AI, deep learning and robots from children into responsible citizens
- What is Agentic AI? Towards action-oriented AI systems
- Top AI trends for 2025 with a human-first AI focus
- CEOs on the obstacles to AI adoption in organizations
- Trends and evolutions in AI and robotics 2025 and beyond
Top image: Shutterstock – Copyright: NicoElNino

